3 GRU
课上讲过GRU可以有效降低梯度消失:
$$\begin{align*}
z_{t} &= \sigma(W^{(z)}x_{t} + U^{(z)}h_{t-1}+b_z)&~\text{(Update gate)}\\
r_{t} &= \sigma(W^{(r)}x_{t} + U^{(r)}h_{t-1}+b_r)&~\text{(Reset gate)}\\
\tilde{h}_{t} &= \operatorname{tanh}(r_{t}\circ Uh_{t-1} + Wx_{t} +b_h)&~\text{(New memory)}\\
h_{t} &= (1 - z_{t}) \circ \tilde{h}_{t} + z_{t} \circ h_{t-1}&~\text{(Hidden state)}
\end{align*}$$
为了与GRU一致,将RNN记作
$$h_{t} = \sigma(r_{t}\circ Uh_{t-1} + Wx_{t} +b_h)$$
a latch
用RNN模拟一个自动机,输出序列的第一个比特。
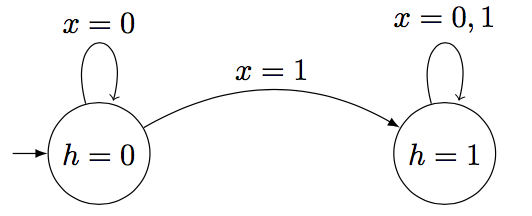
假设初始隐藏状态为0,激活函数替换为indicator函数:
$$\sigma(x)\rightarrow
\begin{cases}
1, & \text{if $x$ > 0} \\
0, & \text{otherwise}
\end{cases}$$
$$\tanh(x)\rightarrow \begin{cases} 1, & \text{if $x$ > 0} \\ 0, & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}$$
推导RNN各参数需要满足的条件。
$$h^{(t)} = \sigma(x^{(t)}U_h+h^{(t-1)}W_h+b_h)$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=0,x^{(t)}=0$时,要让$h^{(t)}=0$则需要
$$\begin{align}
\sigma(b_h)&=0\\
b_h&\leq 0
\end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=0,x^{(t)}=1$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则需要
$$\begin{align} \sigma(U_h+b_h)&=0\\ U_h+b_h&> 0 \end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=1,x^{(t)}=0$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则需要
$$\begin{align} \sigma(W_h+b_h)&=1\\ W_h+b_h&> 0 \end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=1,x^{(t)}=1$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则需要
$$\begin{align} \sigma(W_h+U_h+b_h)&=1\\ W_h+U_h+b_h 0 \end{align}$$
也就是说必须满足
$$\begin{align}
b_h&\leq0\\
U_h+b_h&>0\\
W_h+b_h&>0
\end{align}$$
让$w_r=u_r=b_r=b_z=b_h=0$,用GRU模拟上述自动机。GRU单元简化为:
$$\begin{align}
z^{(t)}&=\sigma(x^{(t)}U_z+h^{(t-1)}W_z)\\
r^{(t)}&=0\\
\tilde{h}^{(t)}&=\tanh(x^{(t)}U_h)\\
h^{(t)}&=z{(t)} \circ h^{(t-1)}+(1-z^{(t)}) \circ \tilde{h}^{(t)}
\end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=0,x^{(t)}=0$时,一定满足$h^{(t)}=0$
$$\begin{align}
z^{(t)}&=\sigma(0)=0 \\
\tilde{h}^{(t)}&=\tanh(0)=0 \\
h^{(t)}&=0
\end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=0,x^{(t)}=1$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则有
$$\begin{align}
z^{(t)}&=\sigma(U_z)\\
\tilde{h}^{(t)}&=\tanh(0)=0\\
h^{(t)}&=(1-\sigma(U_z)) \circ \tanh(U_h)=1\\
\rightarrow U_z &\leq 0 \\
U_h&>0
\end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=1,x^{(t)}=0$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则有
$$\begin{align}
z^{(t)}&=\sigma(W_z)\\
\tilde{h}^{(t)}&=\tanh(0)=0\\
h^{(t)}&=z^{(t)} \circ h^{(t-1)}=\sigma(W_z)=1\\
\rightarrow W_z&>0
\end{align}$$
当$h^{(t-1)}=1,x^{(t)}=1$时,要让$h^{(t)}=1$则有
$$\begin{align} z^{(t)}&=\sigma(U_z+W_z)\\ \tilde{h}^{(t)}&=\tanh(U_h)=0\\ h^{(t)}&=z^{(t)}+(1-\sigma(U_z+W_z)) \circ \tanh(U_h)=1\\ \rightarrow U_z +W_z&>0 \end{align}$$
综合起来,有
$$\begin{align}
W_z&>0\\
U_z&\leq 0\\
U_h&>0
\end{align}$$
b toggle
模拟开关,只要遇到1就切换状态:
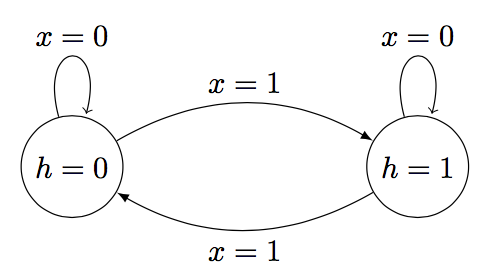
对RNN来讲,当$x=0$时,RNN必须维持上一个状态不变:
$$\begin{align}
0\times w_h+0\times u_h+b_h &\leq0\\
1 \times w_h + 0 \times u_h + b_h &> 0\\
\rightarrow w_h&>0
\end{align}$$
而当$x=1$ 时,RNN必须翻转上一个状态:
$$\begin{align} 0\times w_h+0\times u_h+b_h &>0\\
1 \times w_h + 0 \times u_h + b_h &\leq 0
\\ \rightarrow w_h&<0 \end{align}$$
互相矛盾,所以RNN无法实现开关。
假设$w_r=u_r=b_z=b_h=0$,对GRU来讲先让 $b_r=1$ 去关掉reset gate保持上一个状态。当 $x=1$ 时,$u_z=1,b_z=w_z=0$,就有update gate为1。然后让$\tilde{h}$与$h$异号,有$u_h=0,w_h=-2$。
c 实现GRU单元
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
"""Updates the state using the previous @state and @inputs.
Remember the GRU equations are:
z_t = sigmoid(x_t U_z + h_{t-1} W_z + b_z)
r_t = sigmoid(x_t U_r + h_{t-1} W_r + b_r)
o_t = tanh(x_t U_o + r_t * h_{t-1} W_o + b_o)
h_t = z_t * h_{t-1} + (1 - z_t) * o_t
TODO: In the code below, implement an GRU cell using @inputs
(x_t above) and the state (h_{t-1} above).
- Define W_r, U_r, b_r, W_z, U_z, b_z and W_o, U_o, b_o to
be variables of the apporiate shape using the
`tf.get_variable' functions.
- Compute z, r, o and @new_state (h_t) defined above
Tips:
- Remember to initialize your matrices using the xavier
initialization as before.
Args:
inputs: is the input vector of size [None, self.input_size]
state: is the previous state vector of size [None, self.state_size]
scope: is the name of the scope to be used when defining the variables inside.
Returns:
a pair of the output vector and the new state vector.
"""
scope = scope or type(self).__name__
# It's always a good idea to scope variables in functions lest they
# be defined elsewhere!
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
### YOUR CODE HERE (~20-30 lines)
initFunc = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(uniform=False)
W_r = tf.get_variable('W_r', [self.state_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
U_r = tf.get_variable('U_r', [self.input_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
b_r = tf.get_variable('b_r', [self.state_size,], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0), dtype = tf.float32)
W_z = tf.get_variable('W_z', [self.state_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
U_z = tf.get_variable('U_z', [self.input_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
b_z = tf.get_variable('b_z', [self.state_size,], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0), dtype = tf.float32) ## Recommend on Piazza
W_o = tf.get_variable('W_o', [self.state_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
U_o = tf.get_variable('U_o', [self.input_size, self.state_size], initializer=initFunc, dtype = tf.float32)
b_o = tf.get_variable('b_o', [self.state_size,], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0), dtype = tf.float32)
z_t = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(inputs, U_z) + tf.matmul(state, W_z) + b_z)
r_t = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(inputs, U_r) + tf.matmul(state, W_r) + b_r)
o_t = tf.tanh(tf.matmul(inputs, U_o) + tf.matmul(r_t * state, W_o) + b_o)
new_state = z_t * state + (1 - z_t) * o_t
### END YOUR CODE ###
# For a GRU, the output and state are the same (N.B. this isn't true
# for an LSTM, though we aren't using one of those in our
# assignment)
output = new_state
return output, new_state
d 使用TF内置的RNN模型学习latch
先完成最重要的add_prediction_op
def add_prediction_op(self):
"""Runs an rnn on the input using TensorFlows's
@tf.nn.dynamic_rnn function, and returns the final state as a prediction.
TODO:
- Call tf.nn.dynamic_rnn using @cell below. See:
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/nn/recurrent_neural_networks
- Apply a sigmoid transformation on the final state to
normalize the inputs between 0 and 1.
Returns:
preds: tf.Tensor of shape (batch_size, 1)
"""
# Pick out the cell to use here.
if self.config.cell == "rnn":
cell = RNNCell(1, 1)
elif self.config.cell == "gru":
cell = GRUCell(1, 1)
elif self.config.cell == "lstm":
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(1)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported cell type.")
x = self.inputs_placeholder
### YOUR CODE HERE (~2-3 lines)
preds = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, x, dtype=tf.float32)[1]
preds = tf.sigmoid(preds)
### END YOUR CODE
return preds # state # preds
这里的dynamic_rnn会自动unroll运行sequence_length次,输出pair的第二个元素是cell的state。
然后计算梯度的长度,并在其上进行裁剪:
def add_training_op(self, loss): """Sets up the training Ops. Creates an optimizer and applies the gradients to all trainable variables. The Op returned by this function is what must be passed to the `sess.run()` call to cause the model to train. See TODO: - Get the gradients for the loss from optimizer using optimizer.compute_gradients. - if self.clip_gradients is true, clip the global norm of the gradients using tf.clip_by_global_norm to self.config.max_grad_norm - Compute the resultant global norm of the gradients using tf.global_norm and save this global norm in self.grad_norm. - Finally, actually create the training operation by calling optimizer.apply_gradients. See: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/train/gradient_clipping Args: loss: Loss tensor. Returns: train_op: The Op for training. """ optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=self.config.lr) ### YOUR CODE HERE (~6-10 lines) # - Remember to clip gradients only if self.config.clip_gradients # is True. # - Remember to set self.grad_norm grads_and_vars = optimizer.compute_gradients(loss) variables = [output[1] for output in grads_and_vars] gradients = [output[0] for output in grads_and_vars] if self.config.clip_gradients: tmp_gradients = tf.clip_by_global_norm(gradients, clip_norm=self.config.max_grad_norm)[0] gradients = tmp_gradients grads_and_vars = [(gradients[i], variables[i]) for i in range(len(gradients))] self.grad_norm = tf.global_norm(gradients) train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars) ### END YOUR CODE assert self.grad_norm is not None, "grad_norm was not set properly!" return train_op
用到了TF内置的操作clip_by_global_norm。
通过
python q3 gru.py predict -c [rnn|gru] [-g]
运行,得到RNN|GRU的有|无梯度裁剪的图像。
e 分析图像
RNN
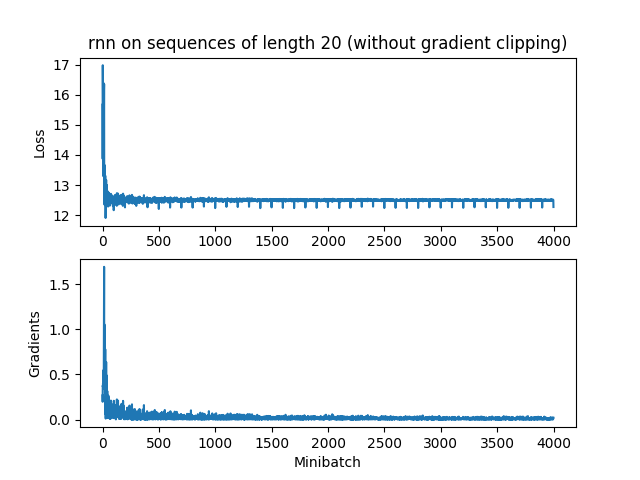
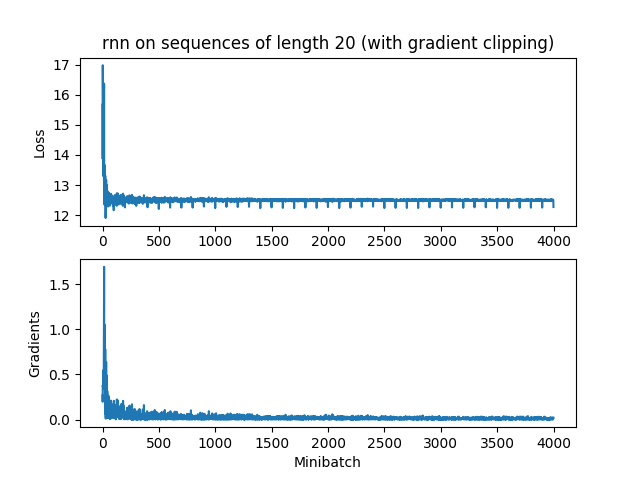
由于RNN梯度消失太快,还没达到最大梯度5就没了,所以裁剪不裁剪都无所谓。
而GRU时不时来个梯度大爆炸,还是很有用的
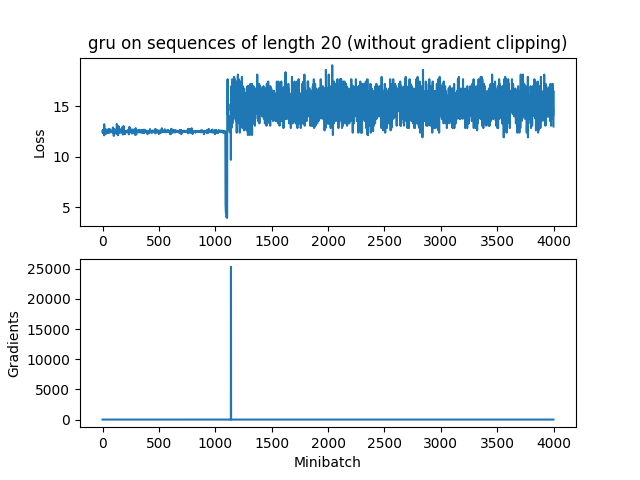
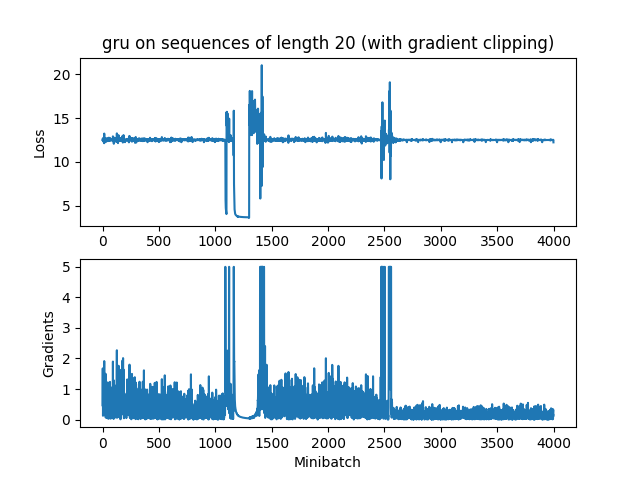
要观测这种现象,与参数初始化关系密切,我的初始化是:
initFunc = tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(uniform=False)
f 运行第二题中的NER模型
这次试用GRU单元
python q2 rnn.py train -c gru
得到差不多的结果
DEBUG:Token-level confusion matrix: go\gu PER ORG LOC MISC O PER 2887 62 39 49 112 ORG 78 1692 67 125 130 LOC 36 99 1855 61 43 MISC 25 48 31 1065 99 O 19 52 11 47 42630 DEBUG:Token-level scores: label acc prec rec f1 PER 0.99 0.95 0.92 0.93 ORG 0.99 0.87 0.81 0.84 LOC 0.99 0.93 0.89 0.91 MISC 0.99 0.79 0.84 0.81 O 0.99 0.99 1.00 0.99 micro 0.99 0.98 0.98 0.98 macro 0.99 0.90 0.89 0.90 not-O 0.99 0.90 0.87 0.88 INFO:Entity level P/R/F1: 0.84/0.85/0.85
彩蛋
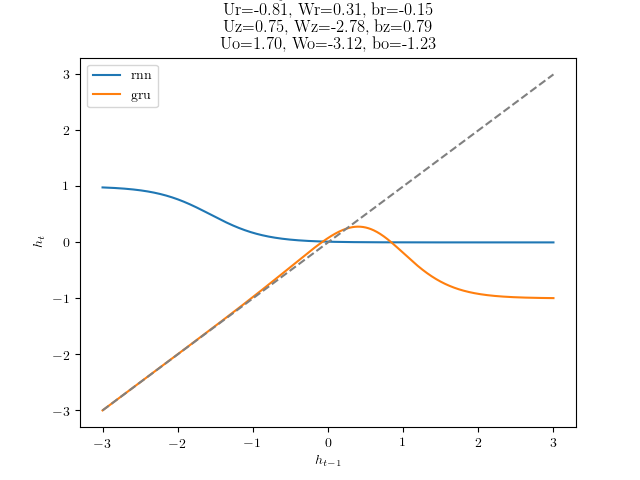
代码中有一个彩蛋,运行
q3_gru.py dynamics
会得到RNN和GRU的上一个隐藏状态和当前隐藏状态的变化图像。原代码其实根本没写完,跑不出RNN的结果。我接着写完后得到:
$x=0$时
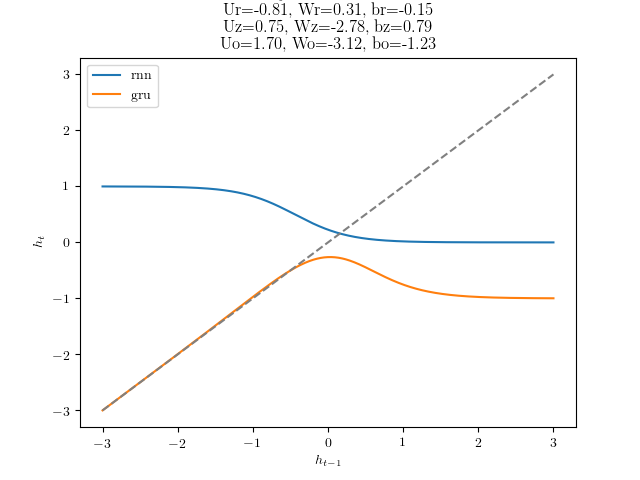
$x=1$时
References
https://github.com/hankcs/CS224n
https://github.com/rymc9384/DeepNLP_CS224N.git
 码农场
码农场
q3_gru.py add_prediction_op() 中dynamic_rnn应该取output而不是state吧?
outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, x, dtype=tf.float32)
output = outputs[:, -1]
preds = tf.sigmoid(output)
代码提示里有写“returns the final state as a prediction”
3 GRU–a latch–ii这道题目的最后一种情况,即h(t−1)=1, x(t)=1,为何h~(t)必须为0?是否可以是这种情况:h~(t)=1, 而z(t)=0,仍然可以使h(t)=1。
博主请抽空指点一下,谢谢
3 GRU a latch ii这个题的最后一种情况,当x_t=h_t=1时,h~t为什么只能为0?h~t和z_t同为1,h_t也能为1,对不对?楼主能抽空答疑一下吗,谢谢。
谢谢博主= =!
因为用的win10,作业要求用python2.7,但没有对应的tensorFlow版本….(也是醉了)
全靠您的代码,我才可以校对
很谢谢