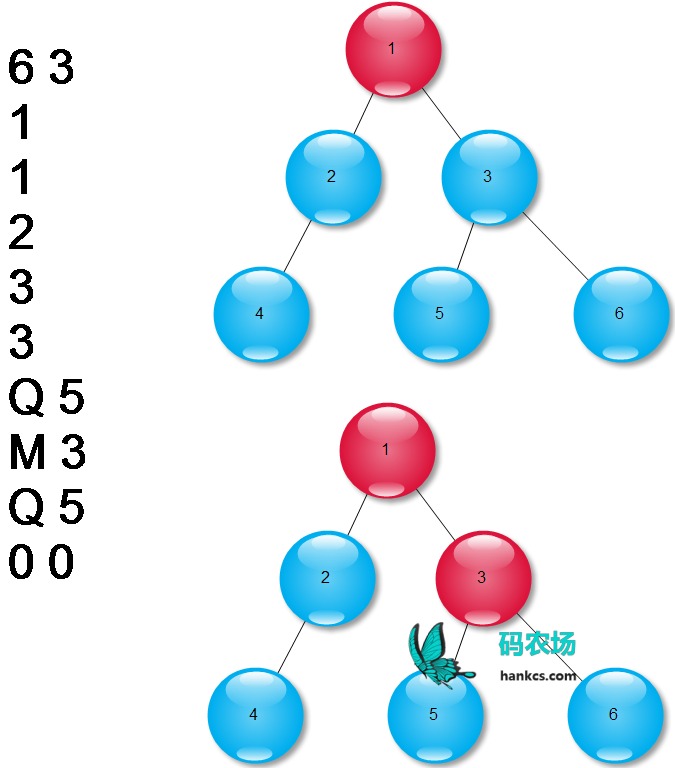

染色祖先:距离某节点最近的染色节点称为祖先,求染色过程中各节点祖先。
2.4 加工并储存数据的数据结构
并查集
稍有些复杂,需要bfs和两棵树。一棵树用来维护并查集,一棵树用来保存原来的树。bfs用来求解每个节点的祖先。也许看到这里你很好奇:既然节点的祖先是用bfs求出来的,那并查集是干什么吃的?这题的复杂之处在于,它是多用例,如果每染色一个节点就跑一遍bfs,那么会TLE。并查集用来省时间的。
思路是先染色,同时用个栈保留这些操作。接着跑一遍bfs,得到祖先的最终状态,并且将祖先相同的节点放入同一个集合中。然后从栈里面弹出操作将节点染回来,“反染色”的过程中,更新并查集和祖先。
注意两点:
-
染色节点的祖先是自己
-
可能存在重复染色,忽略它们
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 并查集相关数据与算法
#define MAX_N 100000 + 16
int parent[MAX_N];
int height[MAX_N];
void init(const int& n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
parent[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
}
int find(const int& x)
{
if (parent[x] == x)
{
return x;
}
else
{
return parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
}
void unite(int x, int y)
{
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y)
{
return;
}
if (height[x] < height[y])
{
parent[x] = y;
}
else
{
parent[y] = x;
if (height[x] == height[y])
{
++height[x];
}
}
}
bool same(const int& x, const int& y)
{
return find(x) == find(y);
}
// End Of 并查集
// 原始的树用它来描述
vector<int> children[MAX_N];
int parent_tree[MAX_N];
bool marked[MAX_N];
int ancestor[MAX_N];
// 每条指令被拆分为 操作 + 目标
stack<char> operation;
stack<int> target;
void bfs(int index, int the_ancestor)
{
queue<int> q_index;
queue<int> q_ancestor;
q_index.push(index);
q_ancestor.push(the_ancestor);
while (!q_index.empty())
{
the_ancestor = q_ancestor.front(); q_ancestor.pop();
index = q_index.front(); q_index.pop();
if (marked[index] == true)
{
the_ancestor = index;
}
ancestor[index] = the_ancestor;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = children[index].begin(); it != children[index].end(); ++it)
{
q_index.push(*it);
q_ancestor.push(the_ancestor);
}
}
}
///////////////////////////SubMain//////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int N, Q;
while (cin >> N, cin >> Q, N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
children[i].clear();
marked[i] = false;
}
marked[0] = true;
int p;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
{
cin >> p; --p;
parent_tree[i] = p;
children[p].push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < Q; ++i)
{
char o;
int t;
cin >> o >> t; --t;
if (o == 'M')
{
if (marked[t])
{
continue;
}
else
{
marked[t] = true;
}
}
operation.push(o);
target.push(t);
}
bfs(0, 0);
init(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
unite(i, ancestor[i]);
}
unsigned long long result = 0;
while (!operation.empty())
{
char o = operation.top(); operation.pop();
int t = target.top(); target.pop();
if (o == 'Q')
{
result += ancestor[find(t)] + 1; // 题目index从1开始
}
else
{
// 执行“反染色”操作,之后这个节点的祖先变为其父节点的祖先
int p = ancestor[find(parent_tree[t])];
unite(t, parent_tree[t]);
ancestor[find(t)] = p;
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////
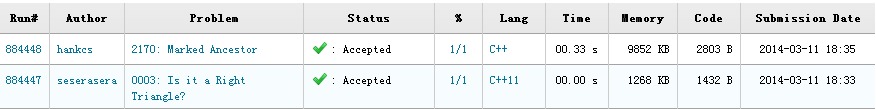
速度还行,从上表看出,AOJ竟然支持 C++11 了!而且与 C++ 视为两种不同的语言!看来第五版的《C++ Primary》里说C++11是一种全新的语言真是诚不我欺也!
![]() 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享:码农场 » AOJ 2170: Marked Ancestor 题解 《挑战程序设计竞赛》
知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享:码农场 » AOJ 2170: Marked Ancestor 题解 《挑战程序设计竞赛》
 码农场
码农场
求您认真去计算一下复杂度,别在这里无知。最坏情况1e10
请问做题用的是什么工具啊?