最小生成树Prim算法
与Dijkstra算法类似,任意挑一个顶点,添加最短边,直至所有顶点都在树中,此时就得到一颗最小生成树了。
证明:
令V为顶点集合,已求得顶点集合为X,V上的最小生成树为T。
假设连接X和V\X的最短边为e,现在需要证明T包含e。
如果T不包含e的话,将e加入T形成一个圈(e是圈的一条边),那么e的两个端点X和V\X之间必定还有一条边f,且f权重比e大,假如删掉f,此时的树成了一颗比最小生成树还小的树,形成矛盾。
Prim算法伪码
MST-PRIM(G, w, r)
1 for each u ∈ G.V
2 u.key ← ∞
3 u.π ← NIL
4 r.key ← 0
5 Q ← G.V
6 while Q ≠ Ø
7 u ← EXTRACT-MIN(Q)
8 for each v ∈ G.Adj[u]
9 if v ∈ Q and w(u, v) < v.key
10 v.π ← u
11 v.key ← w(u, v)
Prim算法复杂度分析
使用最小堆实现Q的话,
-
第5行构造最小堆耗时O(V)。
-
然后EXTRACT-MIN(Q)=O(log V),一共调用V次,所以第6和7行复杂度为O(VlogV)。
-
第8行一共调用2E次(无环图),每次的内层循环复杂度多少呢?第11行修改了最小堆中的一个元素,这个元素需要调整自己的位置,这在最小堆中的代价是O(log V)。
最终复杂度为O(V+VlogV+ElogV)=O(ElogV)。
使用FIBONACCI实现Q的话,
-
相同
-
相同
-
依然调用2E次,但每次复杂度O(1)
最终复杂度为O(V+VlogV+E)=O(E+VlogV)。
为什么我们在上面的最终计算中都忽略了V?因为E的大小是V的平方。
Prim算法的实现
记链接X和V的边的最小权值为mincost[v],添加新顶点u的时候,只需更新u相连的顶点的最小权值即可。
mincost[v] = min(mincost[v] , weight(u, v))。
如果直接遍历mincost找出最小值的话,复杂度为O(|V|2),使用最小堆的话复杂度降低为O(|E|log|V|)。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_V 1024
int mincost[MAX_V]; // 从集合X出发的边到每个顶点的最小权值
bool used[MAX_V]; // 顶点i是否包含在集合X中
int V; // 顶点数
// first 最短路径,second顶点编号
typedef pair<int, int> P;
struct edge
{
int to, cost;
edge(int to = 0, int cost = 0) : cost(cost), to(to) {}
};
// 边
vector<edge> G[MAX_V]; // G[i] 顶点i到G[i].to的权值为G[i].cost
int prim()
{
int res = 0;
memset(mincost, 0x3f, V * sizeof(int));
memset(used, 0, V * sizeof(bool));
mincost[0] = 0;
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P> > que;
que.push(P(0, 0));
while (!que.empty())
{
P p = que.top(); que.pop();
int v = p.second;
if (used[v] || p.first > mincost[v]) continue;
used[v] = true;
res += mincost[v];
for (int i = 0; i < G[v].size(); ++i)
{
edge e = G[v][i];
if (mincost[e.to] > e.cost)
{
mincost[e.to] = e.cost;
que.push(P(mincost[e.to], e.to));
}
}
}
return res;
}
///////////////////////////SubMain//////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// 测试数据
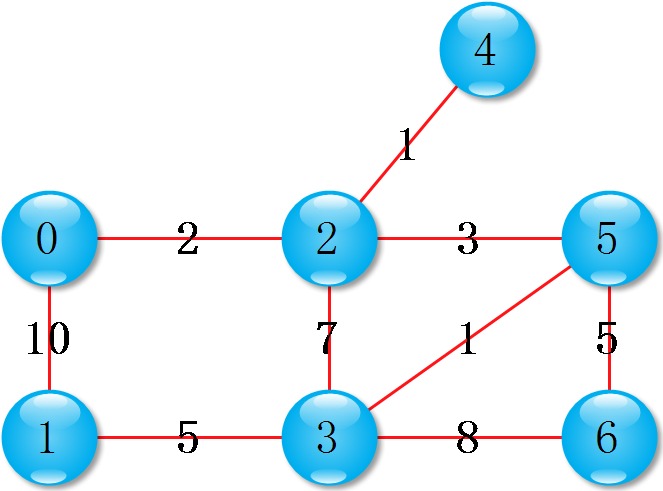
V = 7;
G[0].push_back(edge(1, 10));
G[1].push_back(edge(0, 10));
G[0].push_back(edge(2, 2));
G[2].push_back(edge(0, 2));
G[1].push_back(edge(3, 5));
G[3].push_back(edge(1, 5));
G[2].push_back(edge(3, 7));
G[3].push_back(edge(2, 7));
G[2].push_back(edge(4, 1));
G[4].push_back(edge(2, 1));
G[2].push_back(edge(5, 3));
G[5].push_back(edge(2, 3));
G[3].push_back(edge(5, 1));
G[5].push_back(edge(3, 1));
G[3].push_back(edge(6, 8));
G[6].push_back(edge(3, 8));
G[5].push_back(edge(6, 5));
G[6].push_back(edge(5, 5));
cout << prim() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////
最小生成树Kruskal算法
按照边的权值从小到大尝试加入最小树,如果不产生圈就加进去,否则就扔掉。
关于判断是否产生圈,可以利用并查集来高效地实现。连通的顶点放入一个并查集(连通分量)里,如果一条边e的两个顶点u, v不在同一个连通分量中,那么将e加进来也不会产生圈。
最小生成树Kruskal算法的实现
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_E 1024
// 并查集相关数据与算法
#define MAX_N MAX_E + 16
int parent[MAX_N];
int height[MAX_N];
void init(const int& n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
parent[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
}
int find(const int& x)
{
if (parent[x] == x)
{
return x;
}
else
{
return parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
}
void unite(int x, int y)
{
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y)
{
return;
}
if (height[x] < height[y])
{
parent[x] = y;
}
else
{
parent[y] = x;
if (height[x] == height[y])
{
++height[x];
}
}
}
bool same(const int& x, const int& y)
{
return find(x) == find(y);
}
// End Of 并查集
struct edge
{
int u, v, cost;
edge(int u = 0, int v = 0, int cost = 0) : u(u), v(v), cost(cost) {}
bool operator < (const edge & e2) const
{
return cost < e2.cost;
}
};
edge es[MAX_E];
int V, E;
int kruskal()
{
sort(es, es + E); // 按照权值从小到大排序
init(V);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i)
{
edge e = es[i];
if (!same(e.u, e.v))
{
unite(e.u, e.v);
res += e.cost;
}
}
return res;
}
///////////////////////////SubMain//////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
// 测试数据就不手工填充了,好累( ̄▽ ̄")
cin >> V >> E;
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i)
{
cin >> es[i].u >> es[i].v >> es[i].cost;
}
cout << kruskal() << endl;
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
system("out.txt");
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////
 码农场
码农场
假设连接X和VX的最短边为e,现在需要证明T包含e
这里的VX是什么意思
V去掉X