关于题目的说明请参考http://www.hankcs.com/program/tokyodaigaku.html
这里专注分享我的解法,并接受一切指正。
一些有用的题目提示:
+----+ |Ipwg| |o..u|EFHI KNOR |acto||||| |||| |usw!|VVVV VVVV +----+----+----+----+ | uil|o t|hw: |ak.y|->S | ft |S-to|nw/r|_/ao|->T |scys|iai |o.o |_ttl|->U |tuue|nnn.|ojki|lk. |->V,Y +----+----+----+----+ |GTad| |h/se| |lh r| |CSpF| +----+ Rotate this cube by repeating T,H,E,U,N,I,V,E,R,S,I,T,Y,O,F,T,O,K,Y,O 201^^3 times. a^^b is up-arrow notation.
我绘制的示意图:
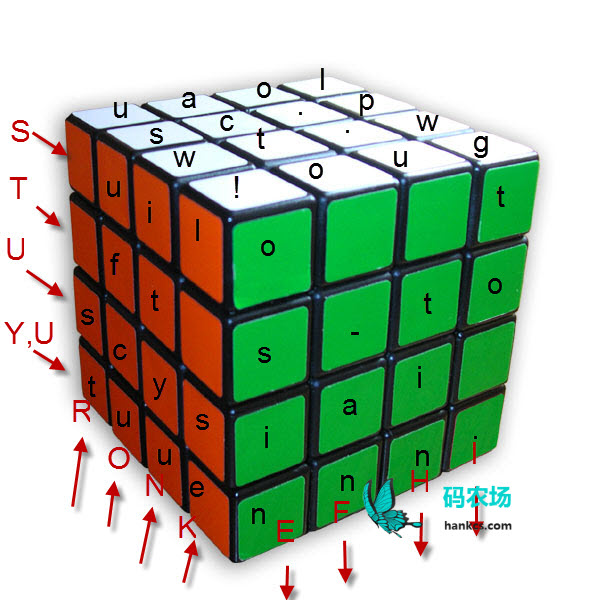
本来我准备利用3d坐标系解决的,但是数据结构和旋转算法很难操控。毕竟你要在控制台展示一个魔方的立体图还是有困难的,于是hankcs采取了将魔方的展开图映射到二位数组,通过指针抽象出一个环形16格的纸片(抱歉我没玩过魔方,不知道如何描述)以及一个4 * 4的面,旋转任意一个指令都至少转动一个环状纸片,也可能还会转动一个面:
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char cube[12][17] = { "Ipwg ",
"o..u ",
"acto ",
"usw! ",
" uilo thw: ak.y",
" ft S-tonw/r_/ao",
"scysiai o.o _ttl",
"tuuennn.ojkilk. ",
"GTad ",
"h/se ",
"lh r",
"CSpF",
};
char bak[12][17];
void ronate(const int& x, const int& y, const bool& clockWise);
const char key[] = "THEUNIVERSITYOFTOKYO";
const unsigned short length = strlen(key);
bool isEqual()
{
for (int y = 0; y < 12; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < 16; ++x)
{
if (bak[y][x] != cube[y][x])
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
void flee(char** pp)
{
char backup[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i)
{
backup[i] = **(pp + i);
}
for (int i = 4; i < 16; ++i)
{
**(pp + i) = backup[i - 4];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
**(pp + i) = backup[12 + i];
}
}
char* getAt(int x, int y)
{
return &cube[y][x];
}
void move_z(char c)
{
char* p[16];
switch (c)
{
case 'E':
ronate(0, 4, true);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[i] = getAt(4, 4 + i);
p[i + 4] = getAt(3 - i, 8);
p[i + 8] = getAt(15, 7 - i);
p[i + 12] = getAt(i, 3);
}
break;
case 'F':
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[i] = getAt(5, 4 + i);
p[i + 4] = getAt(3 - i, 9);
p[i + 8] = getAt(14, 7 - i);
p[i + 12] = getAt(i, 2);
}
break;
case 'H':
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[i] = getAt(6, 4 + i);
p[i + 4] = getAt(3 - i, 10);
p[i + 8] = getAt(13, 7 - i);
p[i + 12] = getAt(i, 1);
}
break;
case 'I':
ronate(8, 4, false);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[i] = getAt(7, 4 + i);
p[i + 4] = getAt(3 - i, 11);
p[i + 8] = getAt(12, 7 - i);
p[i + 12] = getAt(i, 0);
}
break;
default:
cerr << "hmm, invalid key" << endl;
break;
}
flee(p);
}
void printCube()
{
for (int y = 0; y < 12; ++y)
{
cout << cube[y] << endl;
}
}
void move_x(int y)
{
char *p = cube[y];
// copy the last 4 chars
char last[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
last[i] = *(p + 12 + i);
}
// move the last 4 chars to head position
memcpy(p + 4, p, 12);
memcpy(p, last, 4);
}
void move_y(int x)
{
char* p[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[i] = getAt(3 - x + 8, 4 + i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i)
{
p[4 + i] = &cube[11 - i][x];
}
flee(p);
}
void circle(char* p[16], bool clockWize = false)
{
char backup[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 16; ++i)
{
backup[i] = *p[i];
}
if (!clockWize)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
*p[0 + i] = backup[3 + i * 4];
*p[4 + i] = backup[2 + i * 4];
*p[8 + i] = backup[1 + i * 4];
*p[12 + i] = backup[0 + i * 4];
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
*p[3 + i * 4] = backup[0 + i];
*p[2 + i * 4] = backup[4 + i];
*p[1 + i * 4] = backup[8 + i];
*p[0 + i * 4] = backup[12 + i];
}
}
}
void ronate(const int& x, const int& y, const bool& clockWise)
{
char *p[16];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
p[0 + i] = getAt(x + i, y);
p[4 + i] = getAt(x + i, y + 1);
p[8 + i] = getAt(x + i, y + 2);
p[12 + i] = getAt(x + i, y + 3);
}
circle(p, clockWise);
}
void solve(char singleKey)
{
switch (singleKey)
{
// x direction
case 'S':
ronate(0, 0, false);
move_x(4);
break;
case 'T':
move_x(5);
break;
case 'U':
move_x(6);
break;
case 'V':
case 'Y':
ronate(0, 8, true);
move_x(7);
break;
// y direction
case 'R':
ronate(12, 4, false);
move_y(0);
break;
case 'O':
move_y(1);
break;
case 'N':
move_y(2);
break;
case 'K':
ronate(4, 4, true);
move_y(3);
break;
default:
// z direction
move_z(singleKey);
break;
}
}
///////////////////////////SubMain//////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// memcpy(bak, cube, sizeof(cube));
for (int i = 0; i < 3060; ++i)
{
char singleKey = key[i % length];
solve(singleKey);
}
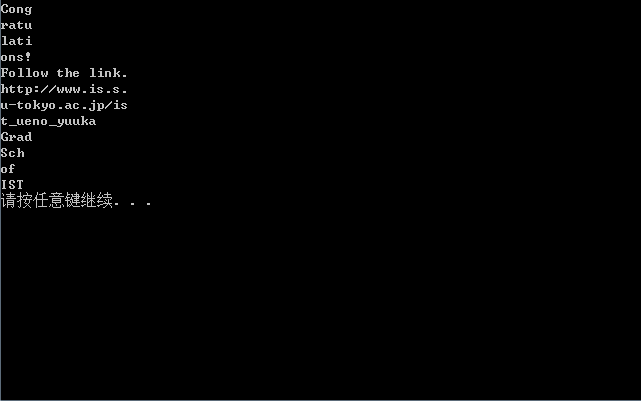
printCube();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////
请注意上面的步数3060是我通过求模算法得出来的,我的算法主要是频繁地找周期,你可以在上文的链接中找到关于它的描述,不是很严密,如果你能提供详细的证明的话,请赐教。
我提供我的那一段找周期的代码:
#pragma warning(disable : 4996)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_LENGTH 1024
///////////////////////////SubMain//////////////////////////////////
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
unsigned long long backup[MAX_LENGTH];
backup[0] = 201 % 6;
cout << backup[0] << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < MAX_LENGTH; ++i)
{
backup[i] = (backup[i - 1] * 201) % 6;
cout << backup[i] << endl;
}
fclose(stdout);
system("out.txt");
return 0;
}
///////////////////////////End Sub//////////////////////////////////
 码农场
码农场