![]()

GCJ 2009 World Finals B : Min Perimeter
极小三角:从n个点中找出3个,使其形成的三角形周长最小。
4.6划分、解决、合并:分治法
平面上的分治法
不断地用垂直分割线把所有点按x坐标分为左右两半,那么极小三角形的顶点无非三种情况:
-
同属左边
-
同属右边
-
分属两边
通过不断地递归拆分子问题,总能将情况1和2拆分为情况3。所以只需考虑第三种情况。(我只想到了这一步,接下来的限定条件参考了analysis)
假设某个子问题的解是p,那么该子问题递归返回到母问题后,母问题就有一个上界p了。由于所有实际要解决的问题都是情况3,情况3中三点分属两边。
于是这三个点在水平和垂直方向都必须满足一些约束,才能成为最优解。
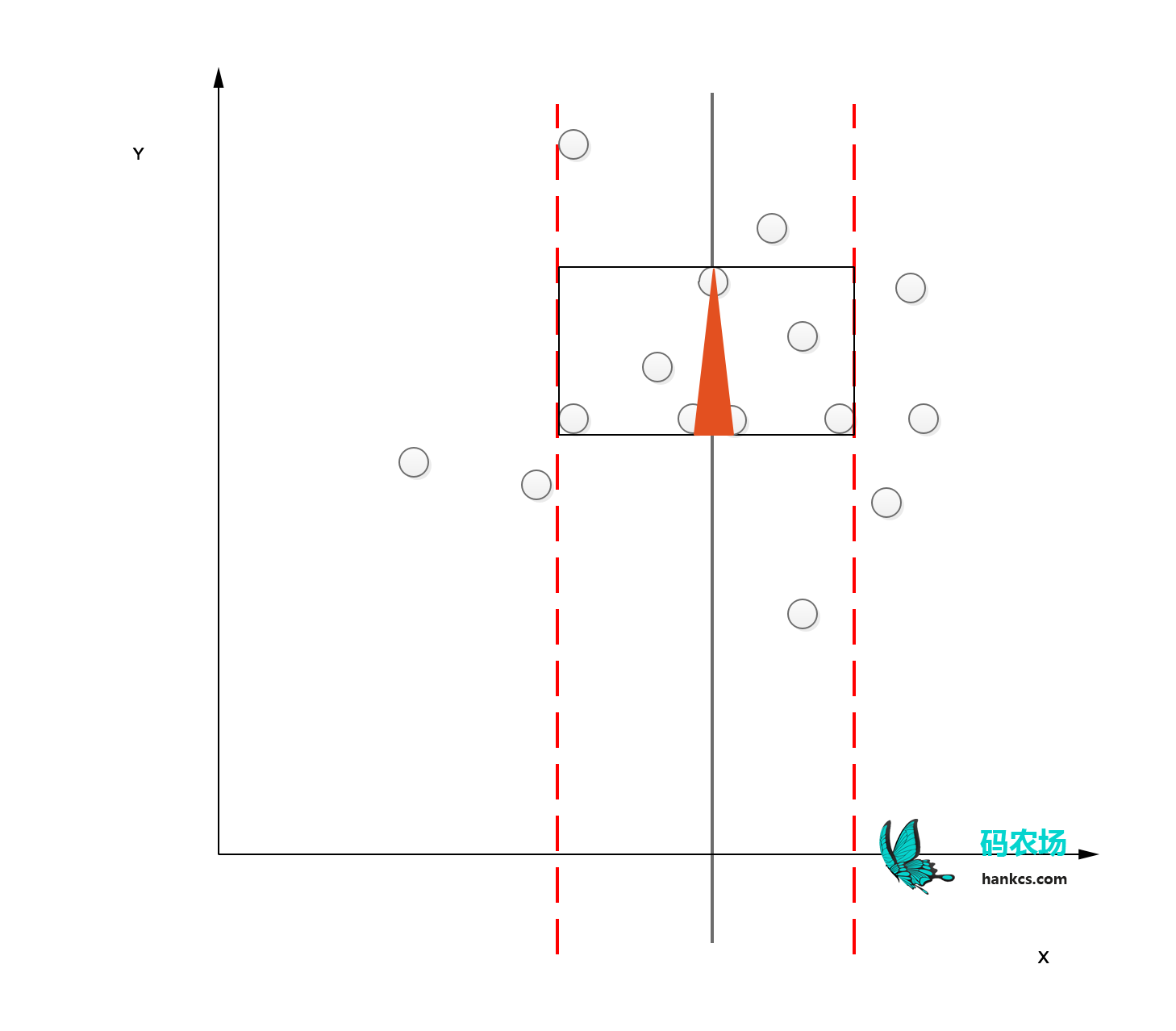
任何一个点离垂直分割线的距离必须小于p/2,否则周长大于p。
另外,最顶端的点离最底端的点的y坐标差必须小于p/2,否则周长大于p。
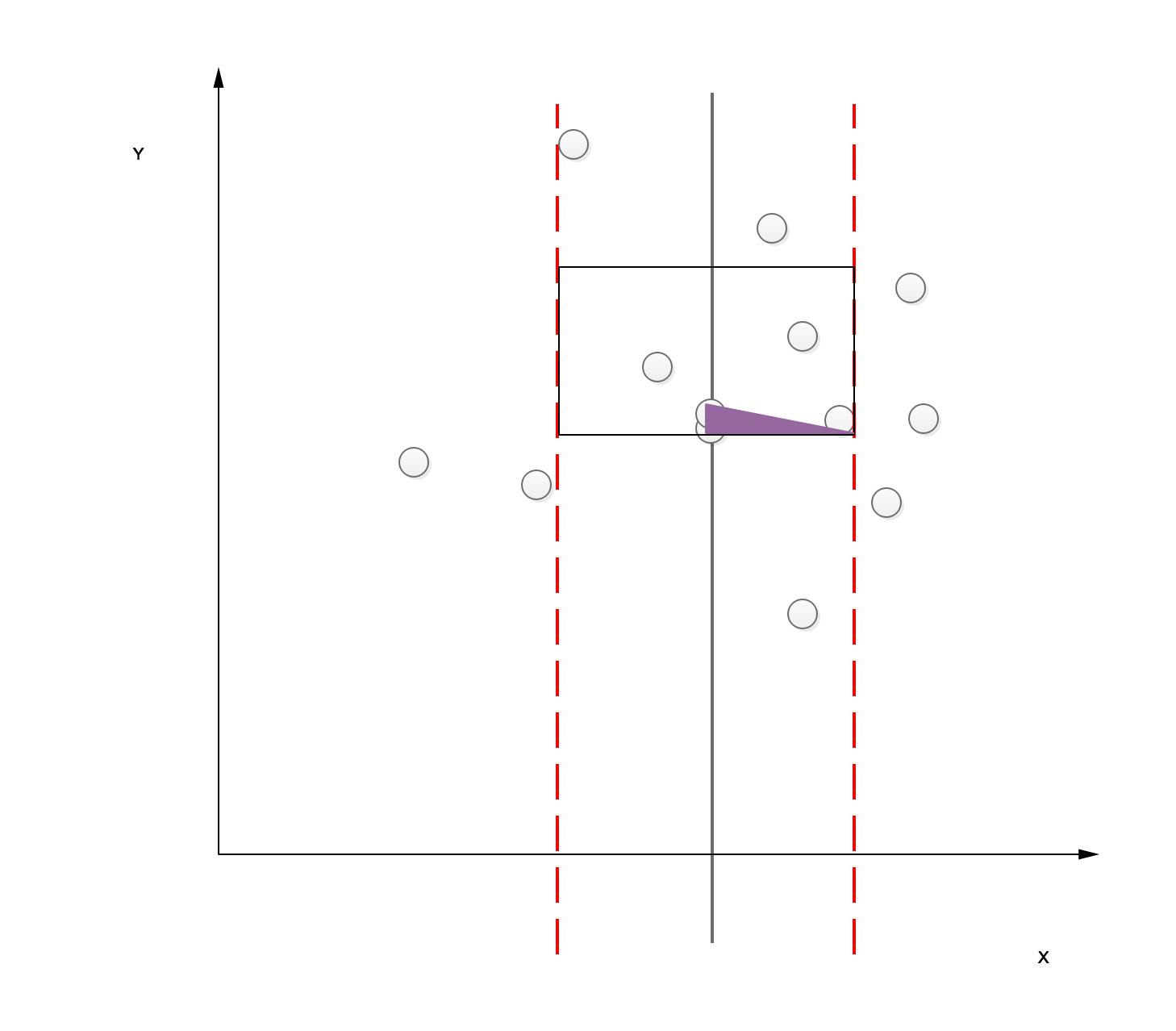
这两个约束实际上构成了一个高度为p/2,宽度为p的矩形框。我们将底端与三角形的第一个顶点对齐,只有矩形框内的点才有可能成为另两个顶点,枚举即可。
比如周长等于p的极端情况1
极端情况2
代码
#include <algorithm>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define REP(i, n) for(int i=0;i<(n);++i)
template<class T>
inline int size(const T &c)
{ return c.size(); }
const int BILLION = 1000000000;
const double INF = 1e20;
typedef long long LL;
struct Point
{
int x, y;
Point()
{}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y)
{}
};
inline Point middle(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
return Point((a.x + b.x) / 2, (a.y + b.y) / 2);
}
struct CmpX
{
inline bool operator()(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
if (a.x != b.x)
return a.x < b.x;
return a.y < b.y;
}
} cmpx;
struct CmpY
{
inline bool operator()(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
if (a.y != b.y)
return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
}
} cmpy;
inline LL sqr(int x)
{ return LL(x) * LL(x); }
inline double dist(const Point &a, const Point &b)
{
return sqrt(double(sqr(a.x - b.x) + sqr(a.y - b.y)));
}
inline double perimeter(const Point &a, const Point &b, const Point &c)
{
return dist(a, b) + dist(b, c) + dist(c, a);
}
double calc(int n, const Point points[], const vector<Point> &pointsByY)
{
if (n < 3)
return INF;
int left = n / 2;
int right = n - left;
Point split = middle(points[left - 1], points[left]);
vector<Point> pointsByYLeft, pointsByYRight;
pointsByYLeft.reserve(left);
pointsByYRight.reserve(right);
REP(i, n)
{
if (cmpx(pointsByY[i], split))
pointsByYLeft.push_back(pointsByY[i]);
else
pointsByYRight.push_back(pointsByY[i]);
}
double res = INF;
res = min(res, calc(left, points, pointsByYLeft));
res = min(res, calc(right, points + left, pointsByYRight));
static vector<Point> closeToTheLine; // 单线程,静态避免创建与销毁
int margin = (res > INF / 2) ? 2 * BILLION : int(res / 2);
closeToTheLine.clear();
closeToTheLine.reserve(n);
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
Point p = pointsByY[i];
if (abs(p.x - split.x) > margin) // 横向离分割线距离p/2以内
continue;
while (start < size(closeToTheLine) && p.y - closeToTheLine[start].y > margin)
++start; // 纵向离底部p
for (int i = start; i < size(closeToTheLine); ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < size(closeToTheLine); ++j)
{
res = min(res, perimeter(p, closeToTheLine[i], closeToTheLine[j]));
}
}
closeToTheLine.push_back(p);
}
return res;
}
double calc(vector<Point> &points)
{
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), cmpx);
vector<Point> pointsByY = points;
sort(pointsByY.begin(), pointsByY.end(), cmpy);
return calc(size(points), &points[0], pointsByY);
}
int main()
{
freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
fprintf(stderr, "Solving\n");
FILE *f = fopen("large.in", "r");
int ntc;
fscanf(f, "%d", &ntc);
REP(tc, ntc)
{
int n;
fscanf(f, "%d", &n);
vector<Point> points;
points.reserve(n);
REP(i, n)
{
int x, y;
fscanf(f, "%d%d", &x, &y);
points.push_back(Point(2 * x - BILLION, 2 * y - BILLION)); // 先乘2,避免待会儿的除法
}
double res = calc(points);
printf("Case #%d: %.15e\n", tc + 1, res / 2);
}
fclose(f);
fclose(stdout);
}
另外谷歌的测试数据太有范了,下载下来是个Java源码。要求自己编译运行,生成相应的数据。
mv B-small-practice.in Input.java javac Input.java java -Xmx512M Input >small.in head small.in 15 3 4 5 0 2 10 7 3 268 316 762 378 235 349 3 mv -f B-large-practice.in Input.java javac Input.java java -Xmx512M Input >large.in head large.in 15 3 433599513 355423475 809635166 973778610 456904466 563063040 4 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 0 0 1000000000 0 0 ll -h *.in 225M large.in 2.0M small.in
真凶残
![]() 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享:码农场 » GCJ 2009 World Finals B : Min Perimeter 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》
知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享:码农场 » GCJ 2009 World Finals B : Min Perimeter 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》
 码农场
码农场
翻 NLP demo的时候搜到了你的博客,16年12月份开 的ML的坑,后面拿着你的书单看,一本一本看没看懂,今天跑过来翻您的博客,受益匪浅,很少有看到那种“没所谓”的去做事了